Cut River Bridge中用于结构健康监测的LUNA技术
The Cut River Bridge along U.S. Route 2 in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula was instrumented with Luna technology as a part of a research project to study the feasibility of a structural health monitoring system (SHMS) for monitoring the structural behavior, evaluating safety, mobility, asset management and planning applications using remote sensors.
The pilot project at the Cut River Bridge is a model that can be used at other bridge locations throughout Michigan, and lessons learned from this project will help MDOT with future implementations of SHMS at other bridge sites.

With the SHMS, the stress in the critical bridge members can be monitored and comparisons between the demand and the capacity of the structural member can be made. The monitoring serves as an early warning system for any potential overstressing in any structural member. This is especially important with a fracture critical structure where little to no visual warning may be given before a failure. When a threshold strain value for safety is surpassed, the system can be designed to alert MDOT and staff respond to a potential concern at the bridge. The SHMS can aid in determining load distribution between structural members, which may be an indication of section loss and changes in stiffness of the structure. With the accurate measurements of forces in the structural members, the ability of the structure to continue safely carrying traffic can be better estimated. This will help MDOT in planning any future repairs and assessing any risks associated with the bridge. The effectiveness of repairs can be monitored by comparing the strain values before and after a retrofit is made, which will also aid in estimating remaining service life.
The bridge was selected for the project due to its stand-alone, remote location without easy access to power, extreme weather conditions at the bridge site, and long distance communication challenges between the bridge and the staffed monitoring location.
切割河桥是三跨,悬臂式甲板桁架桥(密歇根州只有两个悬臂式甲板桥),641英尺长,含有888吨的结构钢,被认为是“骨折临界”结构,这意味着桥的一部分包含钢部件,其故障可能导致桥的一部分崩溃。在2007年I-35W桥崩溃后,密西西比河上的崩溃后,骨折关键结构已收到额外的审查,以防止发生类似的灾难性事件。通常,每两年一次检查骨折临界结构。然而,检查只会在视觉上或通过非破坏性评估(NDE)观察和记录缺陷。没有测量桥的结构构件中的实际物理应力,并且如果构件经历明显的变形,则才能观察到。
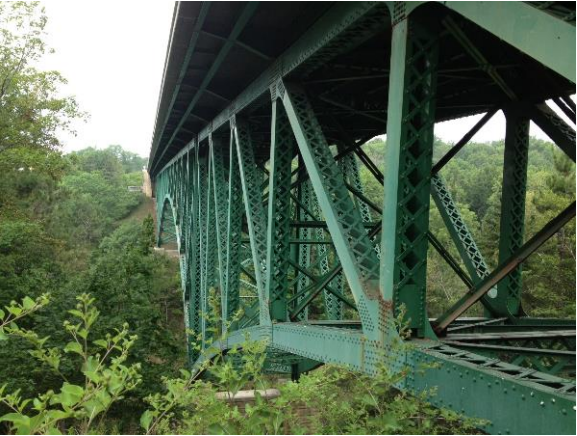
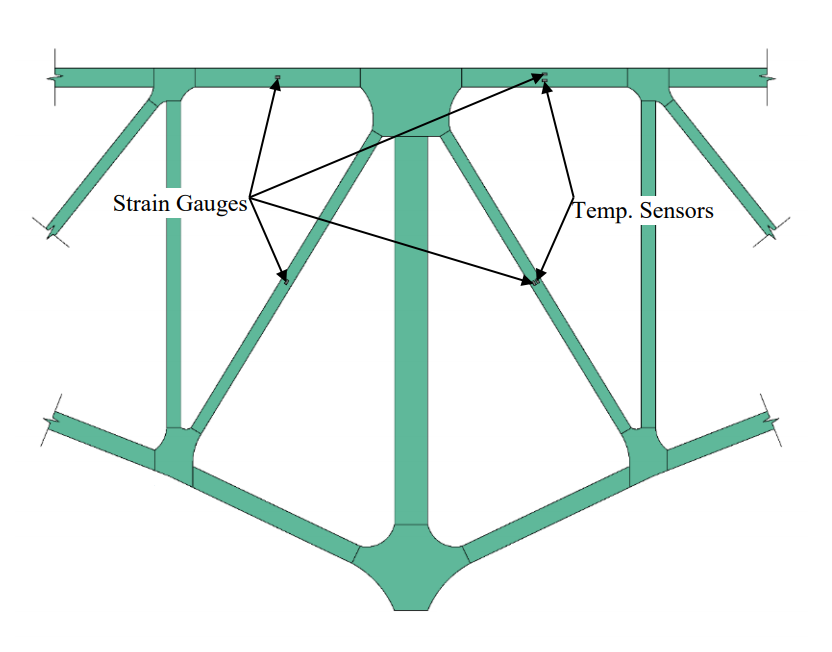
执行结构健康监测(SHM),16 fiber optic Luna strain gauges (below) were installed on several primary tension members in the deck truss. In addition, four temperature sensors were mounted adjacent to four of the fiber optic strain gauges. The temperature sensors aid in correcting for any “drift” of the strain gauges due to temperature effects. In order to understand the truck loads that were crossing the bridge that were causing the observed strains, a weigh-in-motion (WIM) station was placed underneath the roadway approximately two miles east of the bridge. The WIM station provides axle weight and spacing for any truck traveling on the highway.
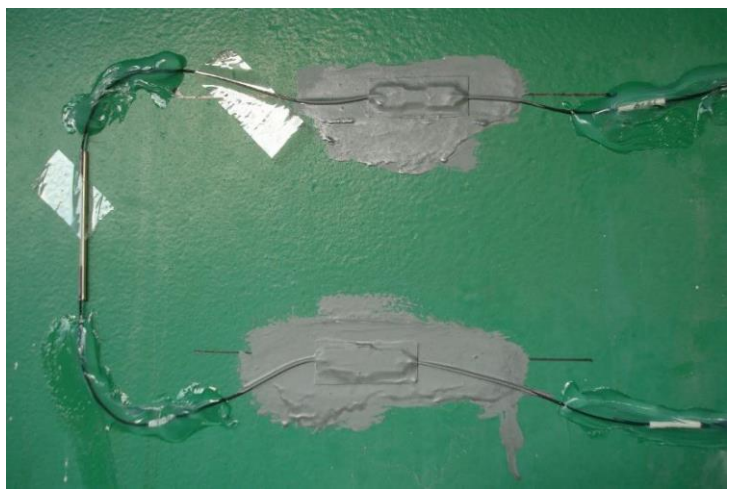
MDOT chose Luna’s fiber optic strain gauges for the many advantages they offered over traditional other strain gage types such as: greater strain range, longer fatigue life, not affected by surrounding electromagnetic waves, and faster sampling rates. The strain readings are corrected for thermal effect through temperature sensors. The strain gauge and the temperature sensors are designed to work together to provide accurate measurements of the strain in the bridge.
应变仪在北部和南桁架的内侧和外侧安装,共有16个16个地点。温度传感器仅在一个对角线和一个顶部水平桁架构件附近安装在应变仪附近。
当光通过光纤电缆和通过传感器时,其波长随着光纤布拉格光栅传感器中的应变而变化,因此在桥梁构件中变化。LUNA(以前的MICRON光学)SM130光学传感询问器连接到传感器并用于连续测量这些波长。它由位于混凝土拱顶中的12V直流太阳能系统供电。来自询问器的数据通过一系列天线传输,最终从带有Internet连接的任何计算机提供。
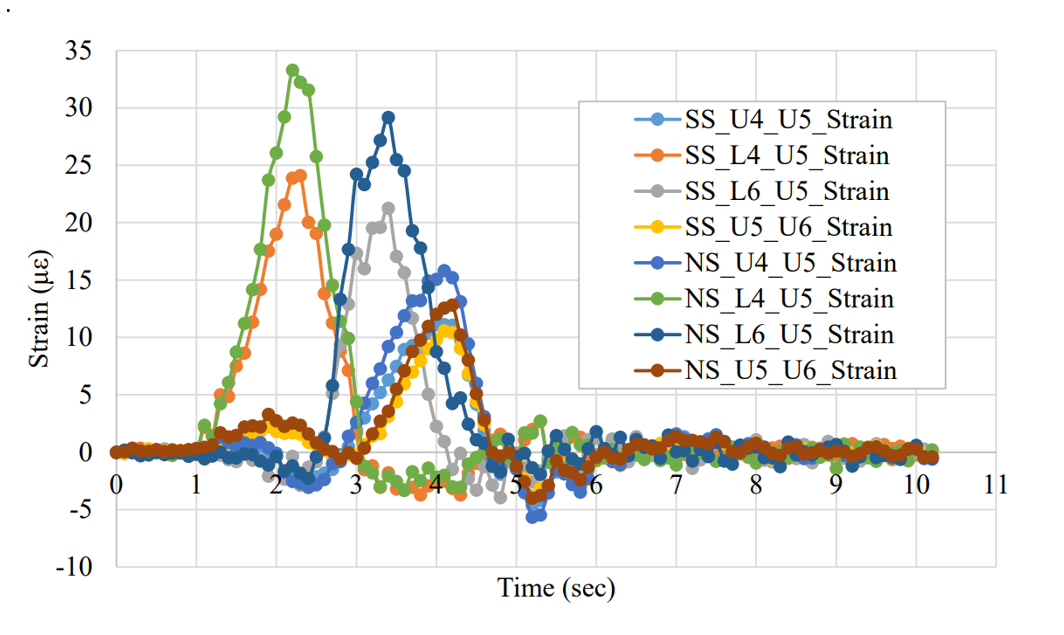
Data from the Cut River Bridge project was collected from a computer located at the bridge engineer’s office but could be collected from any computer with internet access. Another objective of the data collection process was to obtain weights and axle configurations of the trucks that cross the bridge as well as the strain in the bridge members caused by these vehicles. After the data was collected, it was processed to correlate the truck information with the strain information. This information is useful to make correlations between actual loads experienced by the bridge to the design loads according to current AASHTO and MDOT standards.
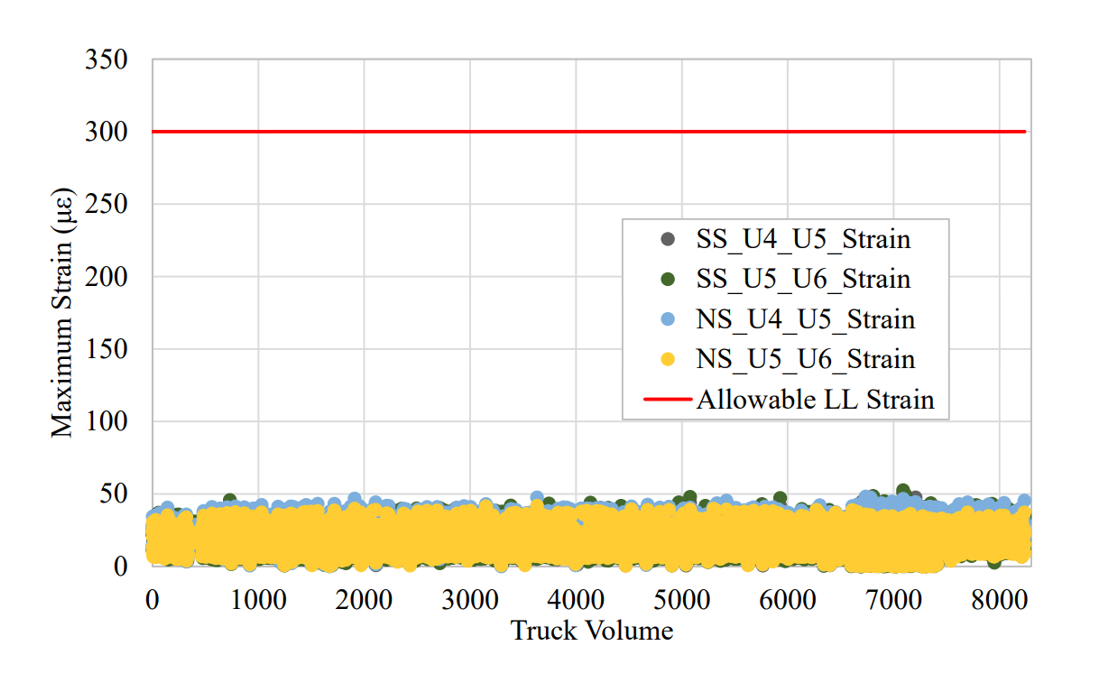
来自桥梁的应变信息用于确定由移动卡车引起的活载应变,然后与最大允许的应变进行比较,以确定桥接构件是否过度了。
Cut River Bridge的试点项目是一种型号,可在密歇根州的其他桥梁位置使用。从这个项目中吸取的经验教训将帮助MDOT在其他桥梁站点的SHM的未来实施。
For information on the Luna sm130, theHYPERION si255interrogator orenlight软件, 联系我们。
阅读密歇根交通部的全部报告,访问this site。